5G is touted to be lightning-fast, apparently allowing for near-instant downloads.
Disappointingly, this does not appear to be the case in the majority of cases! Many users have been dismayed by the results of a 5G speed test.
You may have even wondered at times:
“Why is 5G slower than LTE on my phone?”
Verizon and AT&T utilize Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS), which allows 4G (LTE) and 5G networks to share the same spectrum.
T-Mobile has reserved a portion of its spectrum for low-band 5G deployment.
In either instance, 5G speed can be lower than expected (and slower than LTE networks) due to a number of factors, including:
- The carrier company’s use of current hardware
- Distance from the signal tower
- Compatibility of the smartphone (4G, or 5G phone?)
- Low or mid-band spectrum/frequencies
In this article, we’ll dive into the reasons above and explore different aspects of 5G so that you can better understand your network connection!
Why Is LTE Better Than 5G Right Now?

LTE is the previous-iteration 4G network present on many mobile devices.
5G, in contrast, is the latest upcoming network connection that promises high-speed connectivity and fast downloads.
Mobile providers have been gradually introducing 5G offerings across the United States.
It’s undoubtedly exciting to try out the new 5G connection when you have the opportunity to see if download speeds are what they’ve been claimed to be.
Unfortunately, few people seem to notice a difference in speed. In fact, some users have claimed that LTE was actually superior to 5G and provided a more reliable connection!
Truth be told, hearing this isn’t too surprising.
If you recall the transition from 3G to 4G, you’ll see that it progressed in the same pattern.
Using the 4G network didn’t feel much different to using the 3G network in the beginning.
Everything was pretty much the same, whether it was connectivity, stability, or upload and download speeds.
However, as the weeks turned into months, carrier companies and smartphone manufacturers both made the necessary modifications.
4G networks began to exhibit better speeds, and there a clear distinction between 3G and 4G came to arise.
The same will likely be true for 4G and 5G.
Despite a few changes, carriers have failed to fully modernize their infrastructure to offer broad 5G services as of yet.
Doing so will cost billions of dollars and will be carried in stages. In addition, while the most recent devices may enable 5G, they are still more compatible with 4G networks.
Another aspect to think about is the 5G spectrum as it is currently constructed.
The speeds will most likely be similar (at least right now) because many mobile providers use the same spectrum for 4G and 5G.
For instance, T-Mobile’s low-band spectrum increases range but does not improve speed.
To reach its full potential, 5G technology must operate on mid-to-high-band frequencies. This subsequently necessitates new hardware designed specifically for 5G.
Therefore, 5G will not be as effective as promised until all upgrades are completed.
At this time, the best thing to do is wait and allow the telecom firms and smartphone makers to work their magic behind the scenes.
This is just the beginning!
Is 5G Actually Faster Than LTE?

Long-Term Evolution (LTE) was first introduced and launched in 2009. Despite this, the network took years to deliver on its promises.
History tends to repeat, and the buzz and hype surrounding 5G had been building for some time as well. This time, we were promised something like never before.
However when the time came, 5G was unimpressive- if not outright disappointing! People began to question if it was really quicker than LTE or if the claims were bogus.
5G technically should be quicker than 4G or LTE.
It uses high-frequency bands such as mmWave (millimeter wave) and operates on a separate spectrum. This reduces the time it takes to send data from minutes to mere seconds.
The mmWave high-frequency bands and gear that can sustain these frequencies are critical to the 5G technology’s long-term potential.
While LTE advertised download speeds of up to 150Mbps and upload speeds of up to 50Mbps, the actual download and upload speeds were approximately 20Mbps and 10Mbps, depending on location, carrier, and device.
Similarly, 5G claims a download speed of 10Gbps, but fails to deliver in real-world scenarios (right now, at least).
Furthermore, 5G is still being rolled out and developed so that it can reach its full potential and speed. At the moment, this puts 5G on par with or below LTE.
Speedcheck conducted many tests to demonstrate that 5G gave faster speeds than LTE, on occasion.
AT&T had the fastest download speed, at 53 Mbps, followed by T-Mobile at 47Mbps, and Verizon at 44 Mbps.
However, 5G was still slower than LTE in around 30% of cases.
This demonstrates that while 5G has the potential to be much faster than LTE, it will take some time for it to establish stability and utility.
To boost the speed of the 5G, carrier companies eventually will have to switch from low band to higher band frequencies.
How Much Faster Is 5G Than LTE?
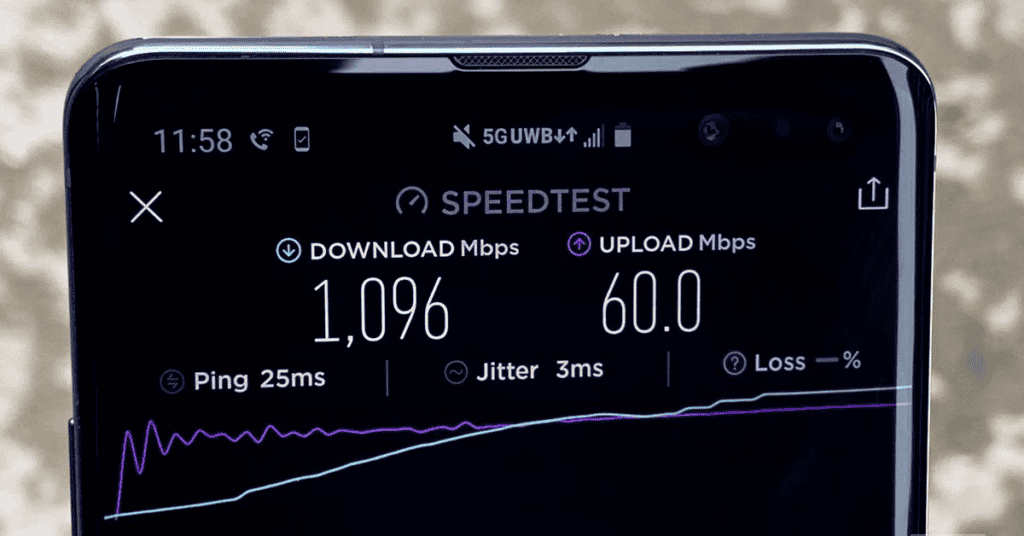
5G is ten times faster than LTE, in theory.
If LTE can deliver roughly 100Mbps, 5G ups that to 1 Gigabit per second.
In addition, the 5G data download rate is expected to reach around 10Gbps at its peak.
It also has a one-millisecond latency, which is the shortest and closest to real-time data transfers. In comparison, LTE has a latency of up to 50 milliseconds in optimal conditions.
However, 5G hasn’t yet reached the point where we can reliably state it’s 10 times faster than LTE; it is still very much in its initial stages.
Given the findings, some users are unsure if they should continue with LTE or switch over to 5G right now.
All we’ll say is that the answer is contingent on your needs.
At this point, it’s probably preferable to use the existing network and wait for the mobile carriers to complete the necessary modifications.
For example, investing in a device like the Samsung Galaxy S21 Ultra- which has 5G but isn’t compatible with 4G– can result in network connectivity issues.
Many smartphone manufacturers are now releasing lower-cost 5G devices. Before paying hundreds of dollars for a device that is essentially the same as LTE, it might be prudent to wait and see first!
Related Questions
Here’s some additional information to help you comprehend 5G in greater depth:
What is a reasonable 5G speed?
The important point here is that the speeds mentioned apply to the mobile network- not the user.
Therefore, depending on the distance between the phone and the tower and the number of connections on the network, the user may only see a fraction of these speeds.
Realistically, the download and upload speeds per user when connected to 5G coverage will be around 100 Mbps and 50 Mbps, respectively.
Can I use 5G for gaming?
Using the same connection, you can theoretically play a game and stream it in near-real-time!
To get the most out of your 5G connection, use either 5G dongles or 5G broadband routers.
In Summary
Why is 5G slower than LTE?
5G is currently slower than 4G LTE speeds in many cases because the carrier companies are either using the same spectrum for both or are relying on low band frequencies to run 5G.
This slows down the network, making it appear to be on par with LTE or even slower (if the phone is far from the tower).
All in all, 5G is still being rolled out across the US and is very much a work in progress. All we can do is sit tight and wait for the companies to make the necessary upgrades to their networking technology!
