So, the question is: Does LTE use more data than other network types?
The short answer to this question is yes. LTE speeds up all data transfers and correspondingly demands a stronger connection to do so.
However, it all depends on the nature of the task you’re performing at the moment.
In other words, LTE is simply a type of connection, just like EDGE or 4G. It cannot use data by merely being turned on.
Instead, these connections allow your phone’s software to utilize them to deliver the result that you’re looking for.
LTE is considerably faster when compared to EDGE. With EDGE, however, you are likely to use fewer data due to the slower speeds.
LTE is fast to the point of allowing you to do as much work while on the move as if you were still using your home Wi-Fi!
Therefore, LTE is both the more efficient and more data-hungry option. As a result, its faster speeds are likely to change your browsing habit- albeit for the better.
In short, when LTE mode is on, web pages and apps load much faster while using up more data.
For most people who upgrade from 3G to LTE, there will be minimal change to their data usage.
However, changing from EDGE to LTE will induce a much more noticeable change. You’ll find that you’ll be able to stream videos and music more smoothly than ever!
Should I Keep LTE On Or Off?

LTE was first rolled out to the market more than a decade ago in 2010; today, nearly all cellular devices support this network type.
To the average user, LTE simply equals faster online connections- with many deeming “4G LTE” as the most advanced form of network.
However, to carriers and operators, LTE represents a more straightforward way of reducing costs while improving the quality of service to users.
LTE is available for all devices with a cellular connection, not only for Android phones or iPhones.
On these devices, you will recognize it by the “LTE” symbol typically at the top right corner of the screen.
When the “LTE” logo appears at the corner of your phone, it means you’re currently connected to LTE instead of inferior networks such as 3G, 2G, or even EDGE.
LTE stands for long-term evolution, and it is designed to offer a high-speed mobile data/internet connection.
As such, it allows you to download large files very quickly, and you also can use it during a video call or when sending someone a large batch of photos all at once.
It is therefore advisable to keep LTE turned on, as you receive superior performance compared to other networks.
Sure, it might cost you some battery life in the process- but that’s just the price of speed.
Therefore it’s a good idea to keep your mobile data turned on until your phone starts to run low on juice, at the very least.
In any case, it’s extremely easy to charge your device nowadays- whether via conventional, wireless, or portable chargers.
It’s also possible to use Low Power mode alongside LTE to prolong battery life as much as possible.
There may be instances where you would want to switch off LTE mode, however.
For example, if you notice you are using a significantly larger amount of data recently and going well over your limit, simply turn off the LTE for a while to avoid a nasty surprise on your phone bill.
The same goes for when you enter low coverage areas. In these situations, you may find your phone rapidly switching between 3G, LTE, or 2G/ EDGE.
Amidst such turmoil, it’s usually wiser to opt for the slower types of networks, as this instability can eat up your battery levels in a matter of hours and cause you to miss important calls, messages, and notifications as a result.
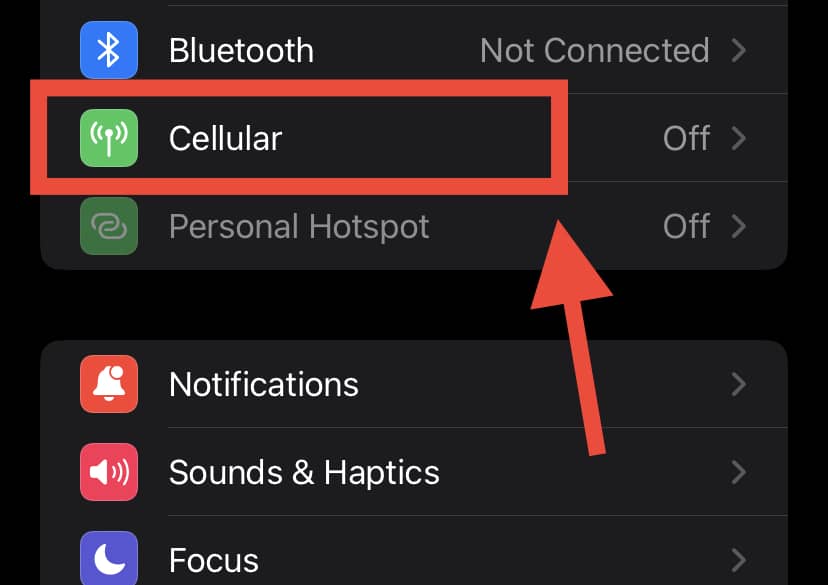
To switch off LTE on an iPhone:
- Go to Settings and select “Cellular,” which is at the top of the list

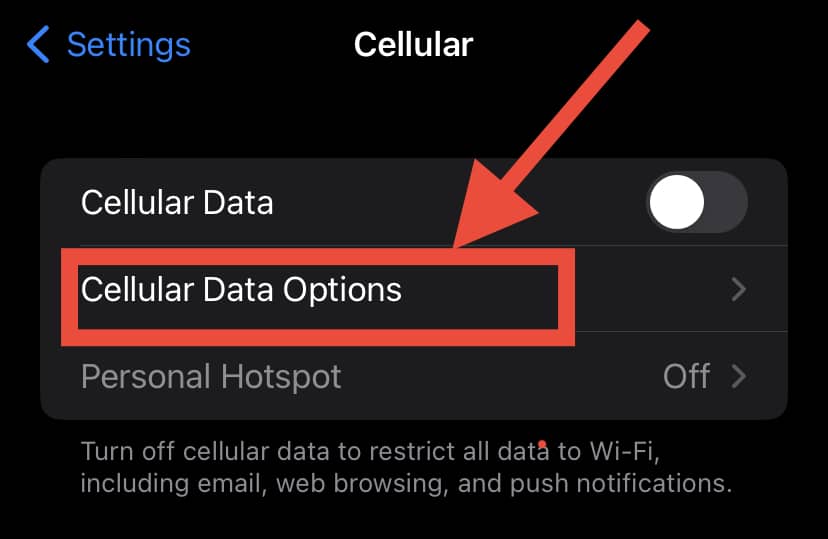
- Select “Cellular data options”
- Enable or switch off LTE. The iPhone allows you to select it for voice data only or for all purposes. So, think ahead and opt for the more useful mode for you in the long run;
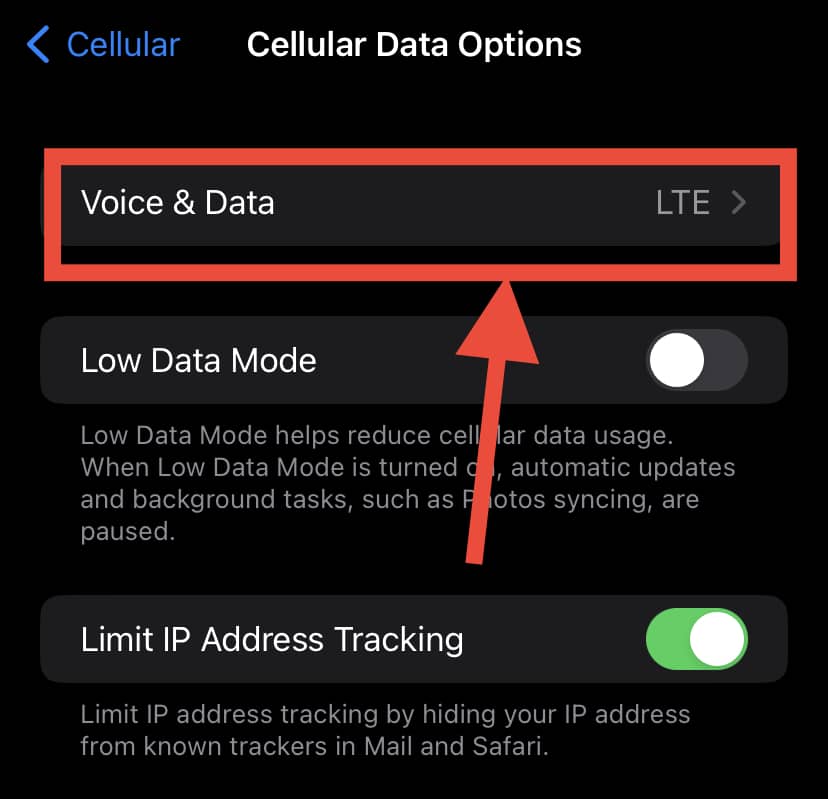
- If you turn off LTE, wait a few moments for it to stabilize and to change to 3G/4G for your connection. The symbols 4G/3G will appear on the top right corner of your iPhone.
- Close the Settings app and continue using your phone with the slower connection.
Does LTE Use Data Or Wi-Fi?

LTE and Wi-Fi are both connection types that allow a user to gain access to the internet.
As such, LTE does not use Wi-Fi; instead, it uses data. LTE relies on radio waves to transmit and function.
To use LTE, you need a service provider that provides 4G coverage in your area. The performance of LTE on your phone likewise depends on your phone’s hardware.
The majority of the latest devices available on the market will support 4G with no problem (with some now even able to connect to 5G!).
A Comparison Between LTE and Wi-Fi

As I’m sure you’re already aware, Wi-Fi is a networking tool that allows internet connectivity to devices within a fixed location. Again, there needs to be a service provider and router to distribute this signal for it to be available.
The data provided by LTE is high-speed and can transfer up to 1GB/s. With Wi-Fi, it all depends on the network’s source.
Wi-Fi connections can be faster than an LTE data connection if you sign up for more powerful network options such as Fiber internet.
LTE is a suitable plan for people who are always on the go, while Wi-Fi is good for the opposite scenario. As such, people who work in one location for extended periods can utilize Wi-Fi more readily.
Finally, the data restriction aspect should also be considered. Depending on your monthly data plan, you’ll likely have a limit on the amount of data you can download from internet browsing and video streaming activities while using LTE.
With Wi-Fi, however, internet access and usage is typically unlimited as long as you have a current contract with a provider.
Does Disabling LTE Use Less Data?

Yes, disabling LTE would decrease your data usage. Therefore if you are on a limited data plan, it might be safer to use 3G (or even 2G) to avoid running out of data suddenly.
This all comes down to practicality and ease of use.
With LTE networks, downloading speeds are much higher; as such, you can achieve more in a much shorter amount of time.
Comparatively, 3G and 2G provide low internet speeds that’ll make you wait just for an initial browser page to load!
Therefore, much of the time you would have otherwise spent watching videos or reading articles on an LTE connection would be inevitably tied up in extended loading times.
If you’re having issues with your data consumption limit, another solution would be to switch off the data connection completely and use Wi-Fi whenever possible. Also, check for any background apps that gobble up data and limit their ability to do so.
It is also important to note that you can disable LTE mode on all calls if you are the type that prefers to communicate through messaging!
LTE allows users the ability to switch off the calling option so that people can only contact them via social media and online messaging.
To achieve this, browse through the Settings, look for the LTE calling option, and switch it off.
While there are undoubtedly disadvantages associated with switching off LTE, it all depends on your needs at the moment.
If speed isn’t a primary goal for the task at hand, simply switch it off! You can turn it back on again and enjoy higher data efficiency at any point by selecting the option in the settings.
Does LTE Use More Battery?

When LTE was first introduced, it used to drain phone batteries in a matter of minutes.
Unfortunately, even after years of development, it still drains the battery relatively quickly when in use.
LTE uses more battery power than its 3G counterpart when transmitting radio waves.
There are several reasons as to why battery usage will be higher when using LTE.
Firstly, as you are able to enjoy faster browsing and can spend more time on the internet; as a result, your screen and processor also exert more strain on the battery.
Additionally, it’s possible to access higher resolution videos when using 4G- something that’s not achievable with 3G or lower.
The longer that your phone runs resource-heavy files such as high-resolution movies, the quicker the battery levels will drain.
Another factor that determines the rate at which your battery becomes depleted is the location that you’re currently in.
Furthermore, the strength of the signal and whether you’re standing in place or moving around also play a significant part.
If you have a strong LTE signal, battery life will tend to last longer as it takes less effort to detect and use. In this regard, a cell signal booster can help to increase signal strength- thus increasing battery life.
When you are in constant motion moving from place to place (such as while driving), you receive cell signals from one cell tower till its range limits- at which point you are then passed on to the next cell tower.
As you might imagine, switching from one cell tower to another uses up battery life quite dramatically. This is especially true when you are moving through an area with 3G and 4G towers!
If that’s the case, a phone will alternate between the two even in a single minute. The switching occurs automatically as you move, and unfortunately, this puts quite the toll on the battery and can drain it rapidly.
In Conclusion
So, does LTE use more data?
Technically speaking: Yes.
Even though the LTE connection itself does not use extra data, the ease of use it provides to the user allows them to read more articles, watch more videos, and play more games.
As a result, a significantly larger amount of data will be used after turning on an LTE mobile data connection!
It would therefore be advisable to switch LTE off if you are on a limited data plan.
If that’s not the case, keep LTE on constantly to reap the benefits of fast internet speeds!
Finally, as you stay on an LTE connection, just keep in mind that the 4G connections tend to put a significant strain on battery life. Pace yourself accordingly!
